Apes Exam Review Weather Climate Land and Aquatic Biomes
A biome is a geographic region that is characterized by a certain type of climate, plant growth, or any other distinguishing characteristic. Biomes are bigger than ecosystems -- a biome describes an unabridged ecosystem on Earth, whereas there tin can be many different ecosystems within that biome.
Terrestrial biomes are any biomes that exist on country. They are ordinarily characterized by institute growth, temperature, and precipitation.

Source: Wikimedia Commons
Tundra
Tundra is a cold and treeless biome that has very trivial low growing vegetation. Tundra is the coldest biome, located in Russia, Canada, Scandinavia, and Alaska. Sometimes, we can also notice tundra on loftier mountains such as the Himalayas. Because there is a layer of permafrost in the soil, tundra can only support shallow-rooted plants such as lichens, mosses, and small woody shrubs.
Source: Unsplash
Boreal Wood
Boreal woods is the second coldest biome. It has mostly coniferous (evergreen) trees that can withstand cold winters and curt growing seasons. Because boreal forests are so cold, nutrients don't decompose easily and so the soils are relatively low in nutrients. We usually see boreal forests in Europe, Russia, and North America.
Source: Unsplash
Temperate Rainforest
Temperate rainforests are a coastal biome that has moderate temperatures and high atmospheric precipitation. Temperate rainforests aren't very common -- they alive on the west declension of North America from northern California to Alaska (think Portland), in southern Chile, and in some areas in Oceania. Since they are close to the bounding main, they have high humidity and mild temperatures. Temperate rainforests also have mainly coniferous trees. Since there is a lot of rain which washes away nutrients, the soil is also low in nutrients, although information technology is better than tundra and boreal forests.
Temperate Seasonal Forest
Unlike the temperate rainforest, the temperate seasonal woods biome has warm summers and cold winters, and information technology has quite a bit of precipitation. They mostly have deciduous broadleaf copse such as maple and oak trees, and since deciduous leaves decompose quickly, they have soil that is very high in nutrients. This means that they are ideal for supporting commercial agriculture, and humans often catechumen these forests into agricultural fields. They are found in eastern United States, Nippon, eastern Australia, and much of Europe.
Woodland/Shrubland
The woodland/shrubland biome has hot, dry out summers and rainy winters. This means that there is a 12-month growing flavour; however, plant growth is restrained by the dry summers and colder temperatures in the winter. In that location are oft droughts and fires in this biome, and so the plants include drought-resistant shrubs such as yucca, scrub oak, and sagebrush. This biome is located in southwestern California, southern Commonwealth of australia, southern South America, and southern Africa.
Temperate Grassland/Common cold Desert
The temperate grassland/cold desert biome has common cold, harsh winters and hot, dry out summers. This biome is very dry out, and the harsh weather makes information technology difficult for plants to abound. This biome also experiences frequent wildfires. However, since there is a long growing flavour and not too many trees, nosotros have converted much of it to agricultural state, either for grazing or for growing wheat. Temperate grasslands are located in the Cracking Plains of North America, the Pampas in S America, and the Steppes in Central Asia and Eastern Europe.
Tropical Rainforest
The tropical rainforest biome is a warm and wet biome that lies near the equator. It experiences little seasonal temperature variation, and it receives a big amount of atmospheric precipitation. Information technology has a lot of vegetation that uses nutrients from the soil, which means that the soil doesn't have that many nutrients. Unfortunately, considering the ecosystem is very productive, a large portion of rainforest is cut down each year to make room for agriculture.
The tropical rainforest has the near biodiversity of all the biomes. It has three singled-out layers of vegetation. The large trees course a woods canopy that covers the rest of the forest. Underneath that, shorter trees make up the subcanopy. Everything else underneath is part of the woods flooring.
Source: Unsplash
Tropical Seasonal Forest/Savanna
The tropical seasonal forest biome has warm forests and distinct moisture and dry seasons. It is located in Central America, south asia, northwestern Commonwealth of australia, and sub Saharan Africa. In areas that take long dry out seasons, like sub Saharan Africa, drier savannas grade. Even though the warm temperatures promote decomposition which leads to rich soil limerick, the dry climate prevents many large plants from growing.
Source: Unsplash
Subtropical Desert
The subtropical desert biome is very hot and very dry. This biome includes the Mojave Desert, Sahara Desert, Arabian Desert, and the Slap-up Victoria Desert. The subtropical desert only promotes succulent and cacti plants, because they are able to store water for long periods of fourth dimension. The soil (sand) is depression in nutrients, and there are barely any plants that live in this biome.
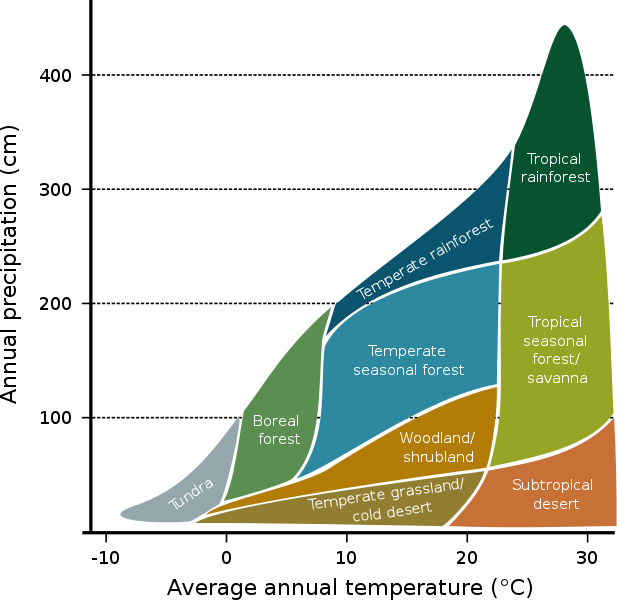
Climate Biome Graph
Since at that place are a lot of biomes, it can be difficult to call back all of them. At that place are a few ways you lot tin group them in society to recall them better.
Biomes are more often than not characterized by both temperature and humidity:
🎥 To learn more nigh biomes, sentinel this stream.
| Temperature | Humidity |
| Tropical = Hot | Rainforest = Moisture |
| Temperate = Moderate | Seasonal Woods/Grassland = Wet and Dry |
| Boreal/Tundra = Cold | Desert/Tundra = Dry |
Resources:
Source: https://library.fiveable.me/ap-enviro/unit-1/terrestrial-biomes/study-guide/itE0pooQYg0jGiYtQnws
0 Response to "Apes Exam Review Weather Climate Land and Aquatic Biomes"
Enregistrer un commentaire